Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2024-07-15 Origin: Site
FDM (Fused deposition modeling) 3D printing, also known as FFF (Fused Filament Fabrication), was introduced in 1989 and is the most common type of 3D printing we see today. It is an extrusion-based additive manufacturing technology, that uses thermoplastic or composite materials, such as ABS, PLA, PETG, and PEI as feedstock.
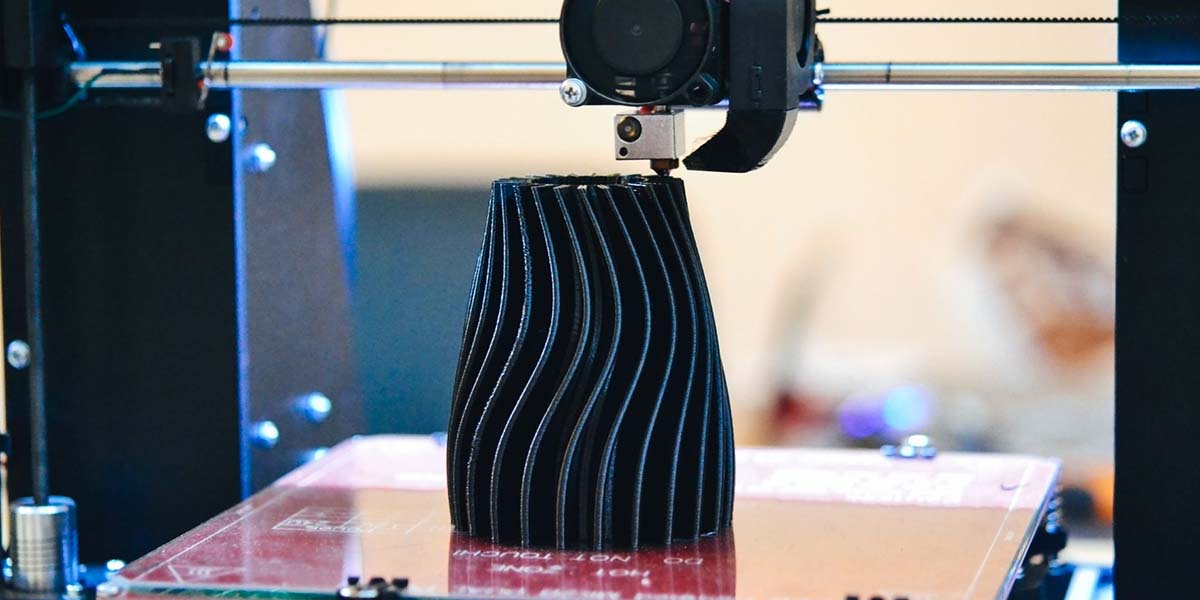
The manufacturing process of FDM is quite straightforward. Before manufacturing an object, a digital design file is uploaded to the machine and is translated into physical dimensions.
Then, the thermoplastic filament is fed by a spool into an extruder, which melts, heats, and extrudes the plastic through a narrow nozzle, forming the print or extrusion head. This extrusion head is attached to a three-axis system that allows it to move across the X, Y, and Z axes.
Following a set of commands from the digital file, the extrusion head moves and works by depositing melted filament layer by layer on a build platform. Generally, the taller the object, the more slices are required, and the longer the lead time will be.
When the print head deposits the filament, the plastic melts onto the previous layer and hardens with cooling fans. This process is continued repeatedly until the parts are completed.
Advantages | Drawbacks |
Cost-effective | Low resolution |
Wide range of materials and colors available | Needs post-processing if fine surface is required |
High production speed | Supporting structures is often required |
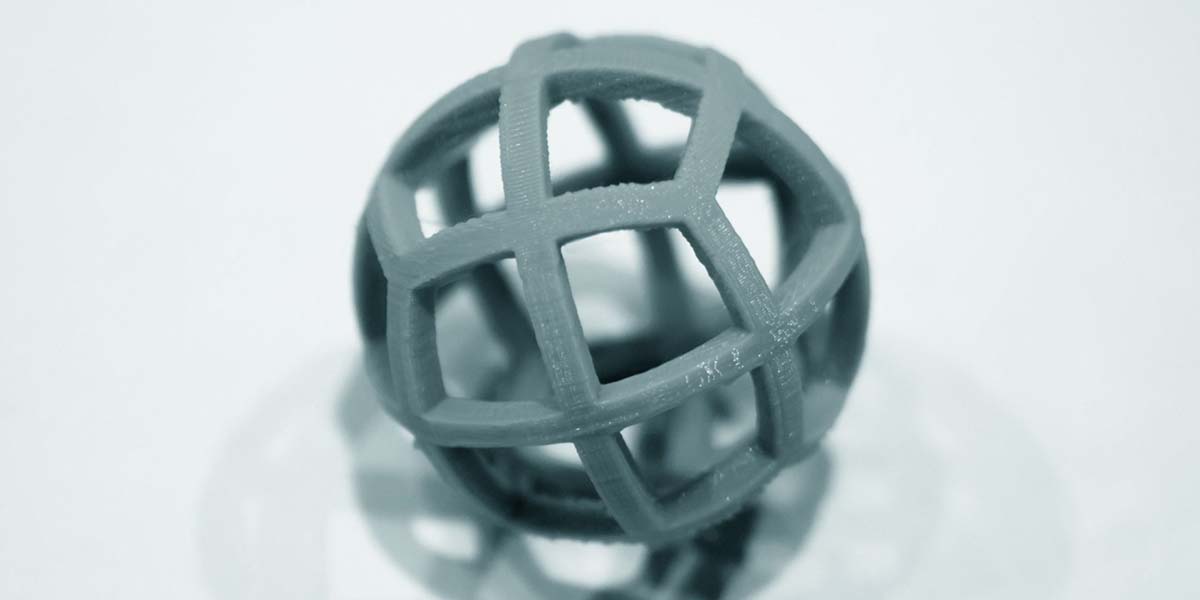
Among all types of 3D printing, FDM is the most commonly used technology for rapid prototyping. Not only because of its cost-effectiveness but also due to its availability of a wide range of highly resistant materials and colors.
However, FDM is not ideal for producing small or detailed parts due to its low resolution. If a smooth or fine surface finishing is required, post-processing is needed as its finished products are likely to come with rough surfaces, resulting in some extra costs.
1. ABS
· High strength
· High temperature resistance
· Prone to warping
2. PLA
· Good visual quality
· Easy to print with
· Minimal impact strength
3. Nylon (PA)
· High strength
· Excellent chemical resistance
· Low humidity resistance
4. PETG
· Food Safe*
· High strength
· Easy to print with
5. TPU
· High flexibility
· Hard to print accurately
6. PEI
· High strength
· Excellent fire and chemical resistance
· High cost
- Healthcare or medical industry
- Automotive industry
- Aerospace industry
- Consumer products industry
- Industrial Equipment Industry
content is empty!